Tag: Robotics
-

Optimal Control of Flow-Induced TRAPs Using Spinning Robots
This project combines optimal control, fluid mechanics, and dynamical systems to design and steer transport and accumulation regions (TRAPs) in fluid environments using spinning robots as flow actuators. By controlling rotation speed, direction, and robot coordination, we aim to generate tailored flow structures that selectively trap floating particles or swimming microorganisms. The theoretical component builds
-
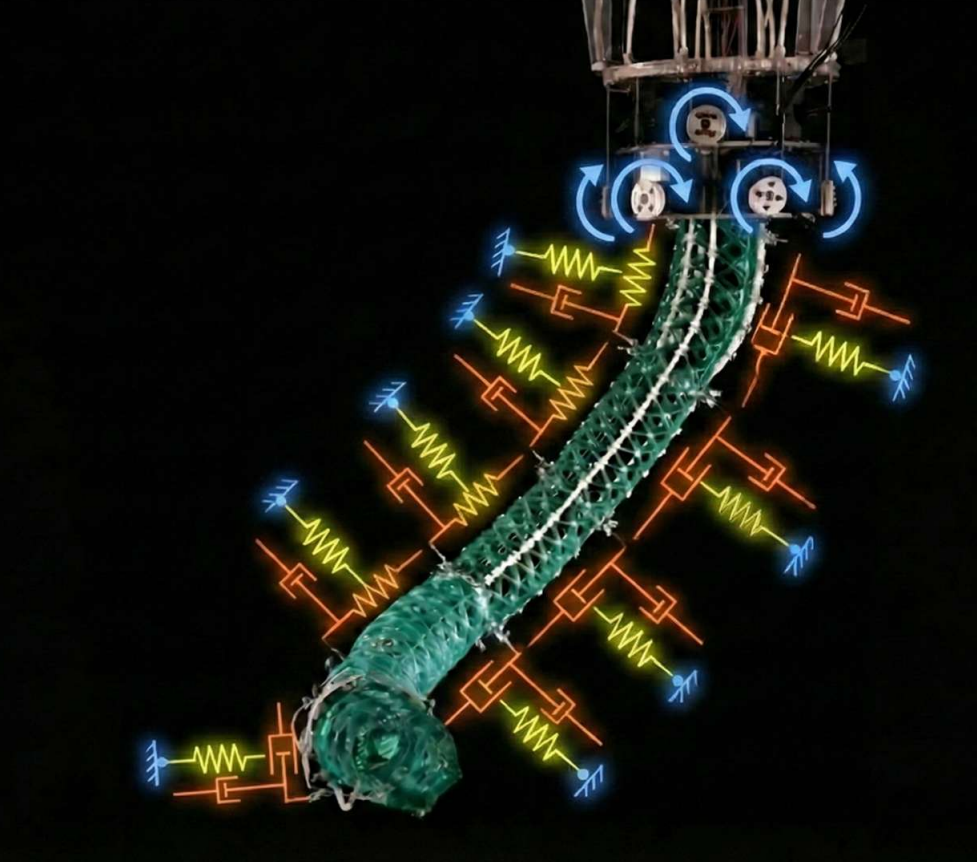
Virtual Model Control of a Soft Compliant Manipulator
Soft continuum robotic arms offer unparalleled dexterity and compliance over rigid bodies, thus facilitating safe and robust interactions with environments. These characteristics make them ideal for diverse applications, such as collaborative robotics or medical contexts. However, due to their virtually infinite degrees of freedom, control of these systems has always been a challenge. Various control
-
Bipedal gait analysis on planetary surfaces
Evaluation of the mechanical cost of transport for a bipedal robot during four bipedal locomotion gaits (walking, running, jumping, and skipping), performed in simulation within three different gravitational scenarios: on Earth, Mars, and the Moon. Contacts Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt German Aerospace Center Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics Münchner Straße 20 82234 Wessling
-
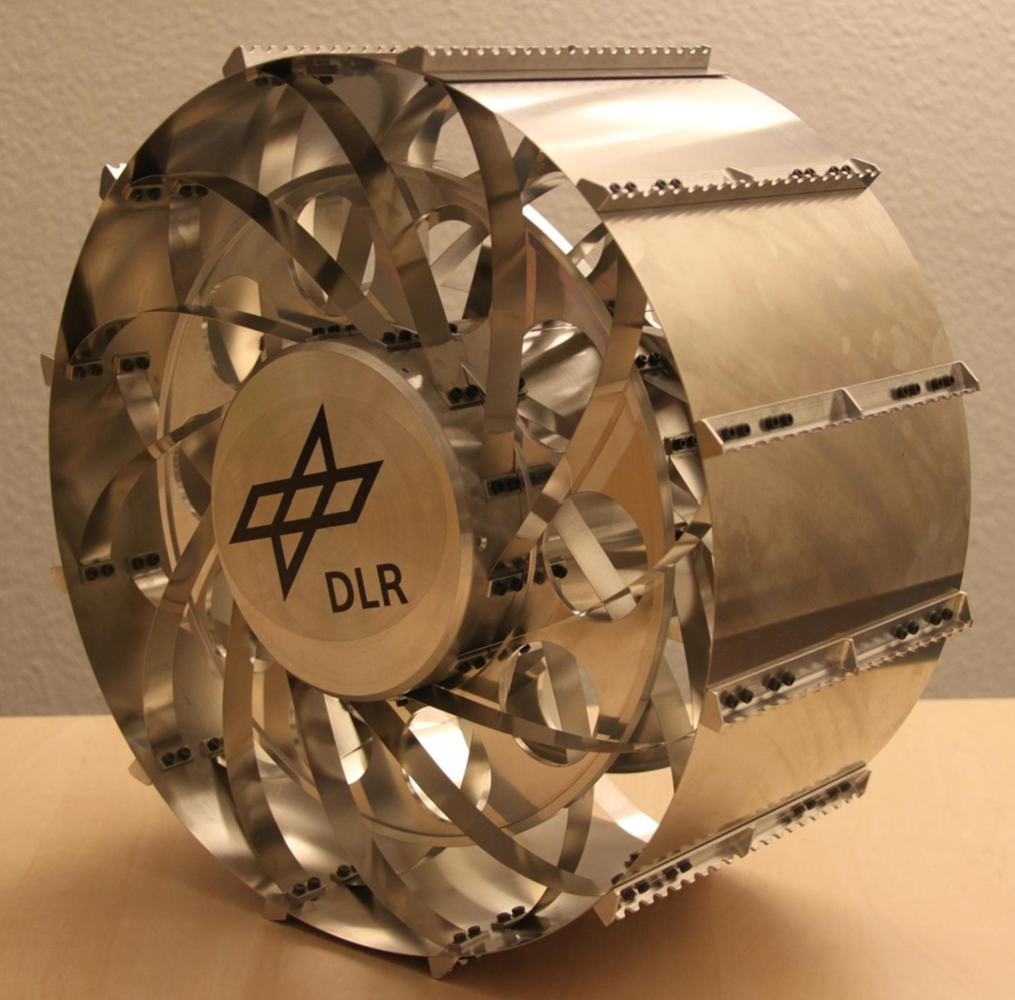

Active spoke wheel
Develop and simulate an active spoke wheel design that is able to climb stairs and navigate smooth terrains with a high energy efficiency. Inspired on the concept of actuated spokes as proposed in hybrid locomotion platforms such as IMPASS (IMPASS: Intelligent Mobility Platform with Active Spoke System | IEEE Conference Publication | IEEE Xplore) Contacts
-
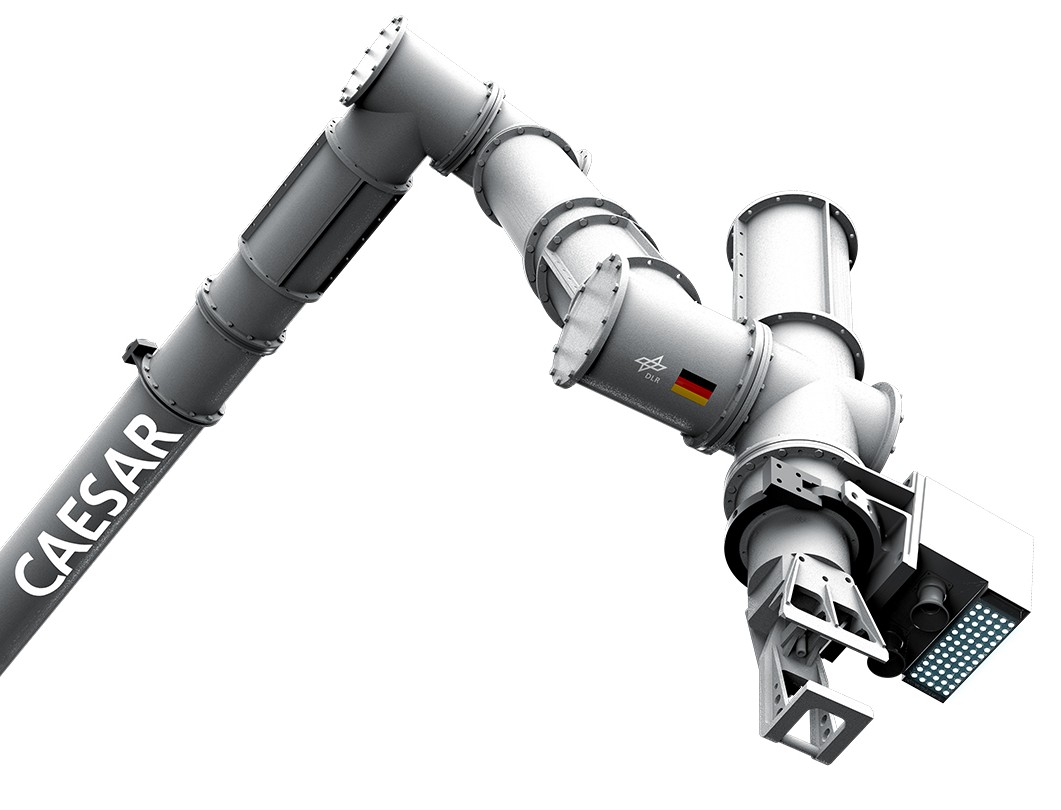
Conceptualization of a Reduced-Complex Cable-Based Gravity Compensation System for Space Manipulator On-Ground Tests
Robotics is primed to play a crucial role in future space missions. By performing tasks such as on-orbit servicing, inspection and de-orbiting, space robotics can enable a sustainable use of Earth’s orbits. The DLR’s Compliant Assistance andExploration SpAce Robot (CAESAR) is a light-weight, dexterous robot with seven degrees of freedom designed for on-orbit servicing in
-

On-Ground Dynamics Parameter Identification and Force Distribution Analysis of a Gravity-Compensated Space Manipulator Robot
Robotics is primed to play a crucial role in future space missions. By performing tasks such as on-orbit servicing, inspection and de-orbiting, space robotics can enable a sustainable use of Earth’s orbits. The DLR’s Compliant Assistance and Exploration SpAce Robot (CAESAR) is a light-weight, dexterous robot with seven degrees of freedom designed for on-orbit servicing
-

Fall Recovery for Quadrupeds
Introduction Legged robots operating in real-world environments are inevitably exposed to disturbances, uneven terrain, and interaction forces that can lead to loss of balance and falls. Robust fall recovery is therefore a critical capability for enabling truly autonomous deployment of quadruped robots in unstructured settings. While traditional approaches rely on hand-crafted reflexes or carefully engineered
-

Fall Recovery for Humanoid Robots
Introduction Humanoid robots are designed to operate in human-centered environments, where unexpected contacts, uneven terrain, and external disturbances frequently lead to loss of balance and falls. Reliable fall recovery is therefore a key capability for long-term autonomous operation and human–robot coexistence. Classical approaches rely on carefully engineered whole-body controllers and pre-defined get-up sequences, which are
-

Actuator Modeling
Introduction Recent advances in GPU-based physics simulation and deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) have enabled the rapid training of control policies for complex, highly articulated robots such as quadrupeds and humanoids. Parallelized simulators now make it possible to obtain policies that transfer to hardware in a matter of minutes of simulated experience [1]. Despite this progress,
-

VLAs for Navigation
Introduction Vision-Language-Action (VLA) models have recently emerged as a powerful paradigm for grounding natural-language instructions in perception and control, enabling robots to execute high-level commands specified in human-friendly terms. In this project, we consider a navigation setting in which a mobile robot (Unitree GO2) receives an egocentric RGB-D observation together with a short natural-language instruction
