Tag: nonlinear dynamics
-

Optimal Control of Flow-Induced TRAPs Using Spinning Robots
This project combines optimal control, fluid mechanics, and dynamical systems to design and steer transport and accumulation regions (TRAPs) in fluid environments using spinning robots as flow actuators. By controlling rotation speed, direction, and robot coordination, we aim to generate tailored flow structures that selectively trap floating particles or swimming microorganisms. The theoretical component builds
-

Multi-Objective Control Synthesis for Floating Wind Turbines
We are looking for a motivated and passionate student to contribute to our research in the field of wind energy and to work on a topic with strong scientific and industrial relevance. Floating wind turbines are complex systems, in which aerodynamics, hydrodynamics, structural dynamics, and control systems are strongly coupled. This multi-physics interaction makes the
-
Topology Optimization in nonlinear dynamics: internal and parametric resonances
Topology optimization techniques for the design of MEMS devices in a linear dynamics framework have already been studied in several works in the literature. However, since there is no control of the degree of nonlinearity of the structure during the optimization process, the outcome of these routines often departs significantly from linearity. The consequence is
-
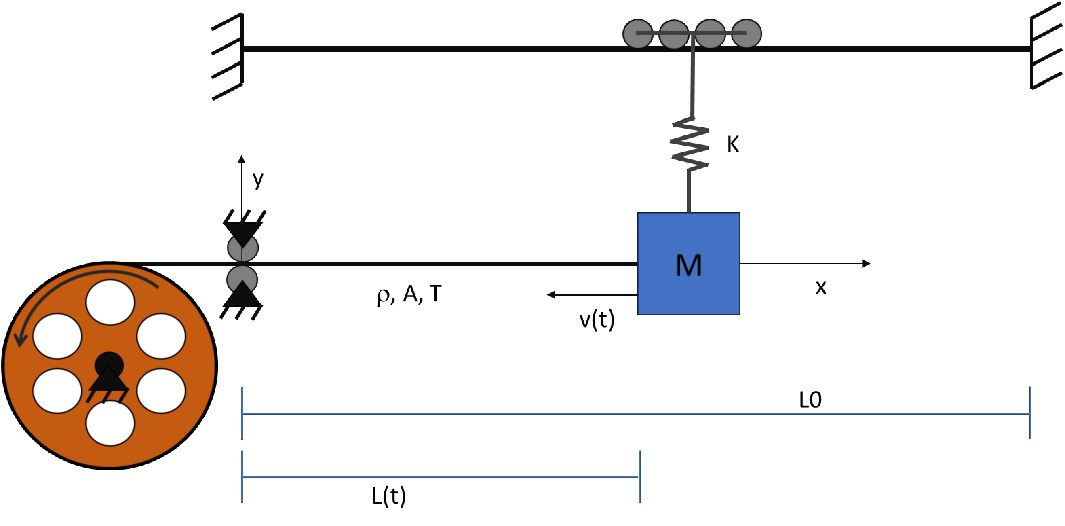
Dynamics of an aerial cableway through a time-varying meshing finite element approach
Ropeways have been used intensively for transportation of goods and people since the early nineteenth century. To study the nonlinear effects of the forces acting on the carrying cable, and how they affect the static and dynamic behaviour of the plant, a finite element model with a time-varying mesh has been developed. The system modelling
-
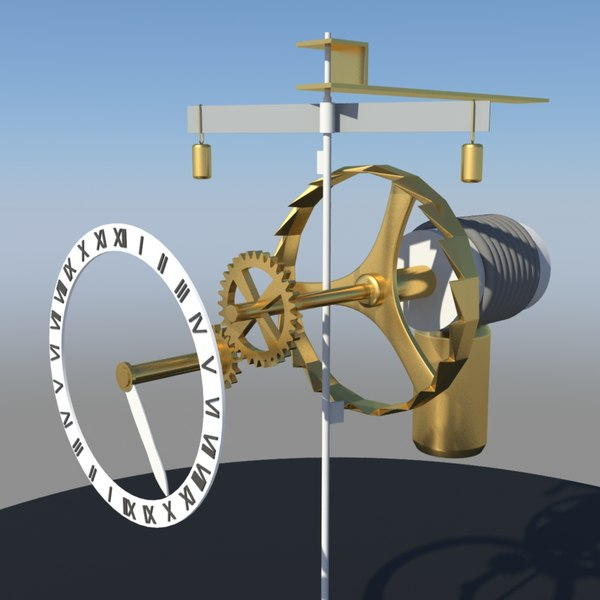
Multibody simulation of medieval mechanical clock
Background and MotivationThe verge-and-foliot escapement is among the earliest mechanical regulation mechanisms, yet its motion and timekeeping performance remain challenging to predict quantitatively because the device operates through intermittent contact between the crown wheel teeth and the pallets mounted on the verge. From an engineering standpoint, this makes the system highly sensitive to geometry, inertia
-
Non-linear analysis of powertrain torsional vibration accounting for backlash
This thesis investigates the non-linear torsional vibration behavior of automotive powertrains, explicitly accounting for backlash effects in transmission components. A lumped-parameter dynamic model is developed to represent dead-zone non-linearities, intermittent contact, and impact phenomena. Time- and frequency-domain analyses are performed to study the influence of operating conditions, torque excitation, and system parameters on the dynamic
-
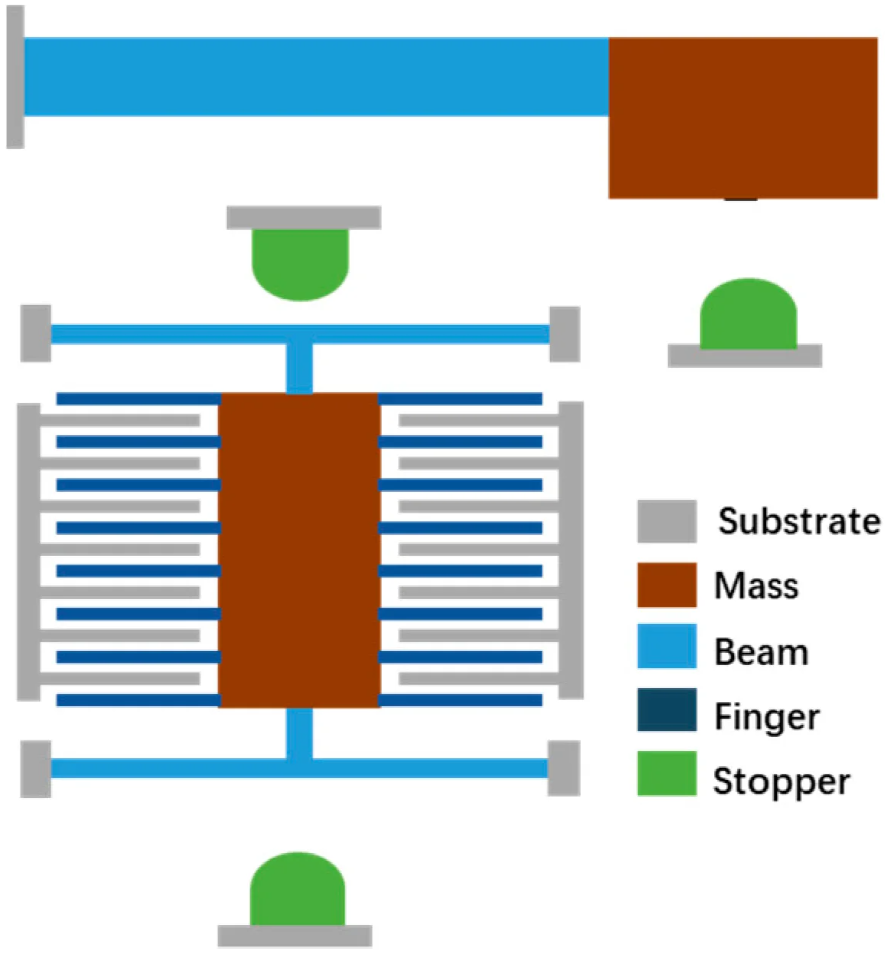
Mechanical nonlinearities (Geometric or Contact) in inertial MEMS sensors
Mechanical nonlinearities play an important role in inertial MEMS sensors and cannot be avoided. The trend to push the performance to the limits caused second-order nonlinear effects to become a critical phenomenon that must be considered: these effects are already visible and characterized on mass production devices. External shocks and vibrations could also induce other
-
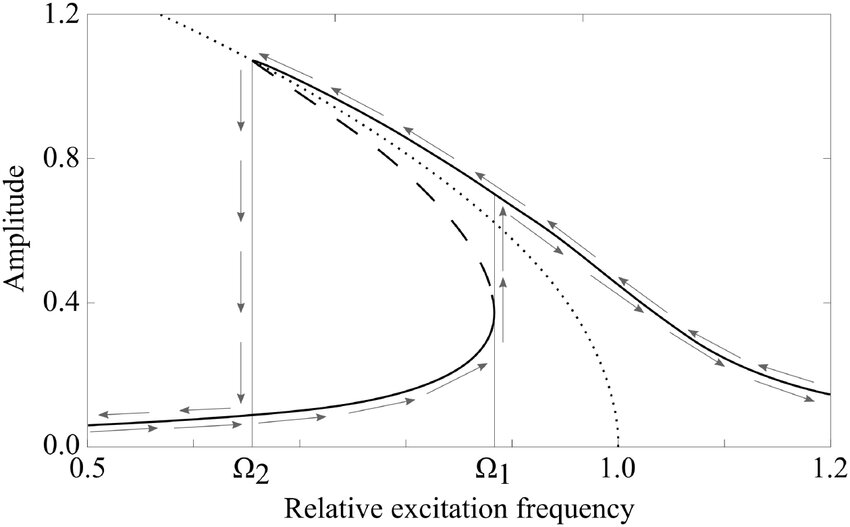
Experimental characterization of nonlinear motion of MEMS resonators
Mechanical nonlinearities play an important role in inertial MEMS sensors, in particular due to geometrical and process constraints. The trend to push the performance to the limits caused second-order nonlinear effects to become a critical phenomenon that must be taken into account: these effects are already visible and characterized on mass production devices. Several methods
-
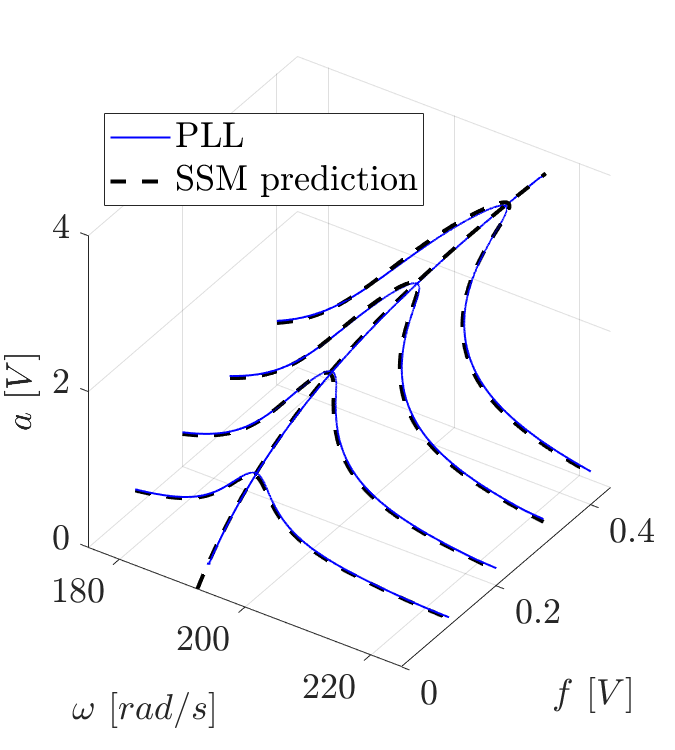
SSM-enhanced Control-Based Continuation (CBC)
In this project we aim to experimentally determine the backbone and the frequency response of a system using Control Based Continuation. CBC consists, loosely speaking, in creating a phase controller (PLL, Phase-Locked Loop) to lock a system at resonance (90°) and then extract the backbone by increasing the forcing with continuation algorithms, typical of numerical
-

Contact dynamics in inertial MEMS sensors
Nowadays, mechanical robustness is a key spec for inertial MEMS sensors. The contacts occurring in silicon structures are a relevant problem that may generate dangerous particles or even cause the breakage of the MEMS sensor. Despite these critical phenomena impacting the sensor’s manufacturing and lifetime functionality, the modeling approaches currently adopted are too simplified. The
