Tag: DLR
-
Bipedal gait analysis on planetary surfaces
Evaluation of the mechanical cost of transport for a bipedal robot during four bipedal locomotion gaits (walking, running, jumping, and skipping), performed in simulation within three different gravitational scenarios: on Earth, Mars, and the Moon. Contacts Deutsches Zentrum für Luft- und Raumfahrt German Aerospace Center Institute of Robotics and Mechatronics Münchner Straße 20 82234 Wessling
-
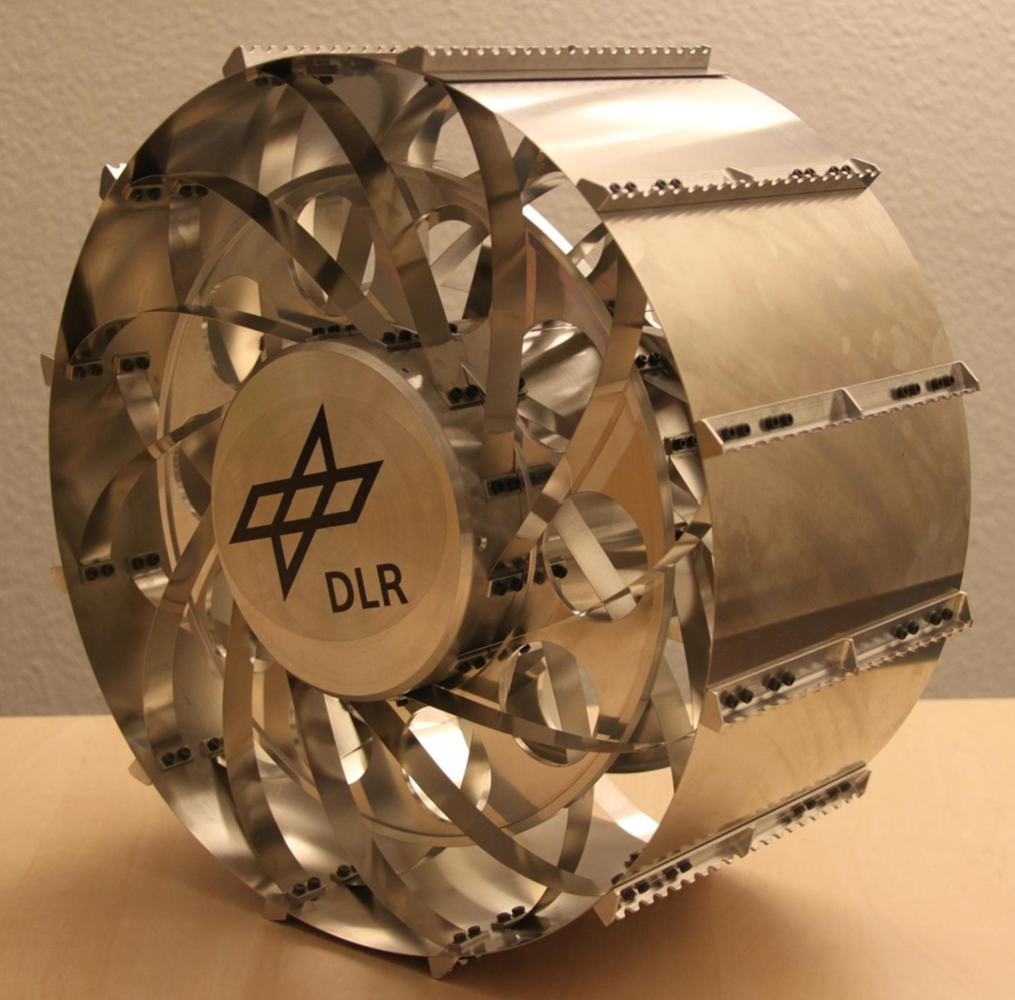

Active spoke wheel
Develop and simulate an active spoke wheel design that is able to climb stairs and navigate smooth terrains with a high energy efficiency. Inspired on the concept of actuated spokes as proposed in hybrid locomotion platforms such as IMPASS (IMPASS: Intelligent Mobility Platform with Active Spoke System | IEEE Conference Publication | IEEE Xplore) Contacts
-
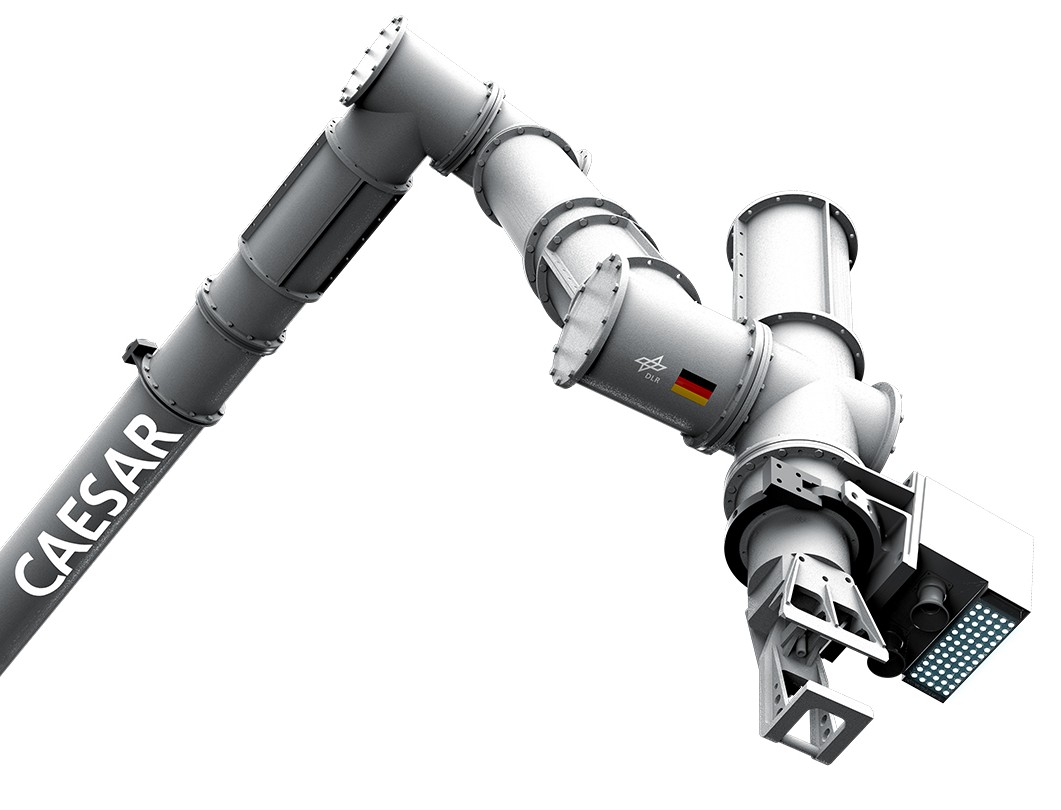
Conceptualization of a Reduced-Complex Cable-Based Gravity Compensation System for Space Manipulator On-Ground Tests
Robotics is primed to play a crucial role in future space missions. By performing tasks such as on-orbit servicing, inspection and de-orbiting, space robotics can enable a sustainable use of Earth’s orbits. The DLR’s Compliant Assistance andExploration SpAce Robot (CAESAR) is a light-weight, dexterous robot with seven degrees of freedom designed for on-orbit servicing in
-

On-Ground Dynamics Parameter Identification and Force Distribution Analysis of a Gravity-Compensated Space Manipulator Robot
Robotics is primed to play a crucial role in future space missions. By performing tasks such as on-orbit servicing, inspection and de-orbiting, space robotics can enable a sustainable use of Earth’s orbits. The DLR’s Compliant Assistance and Exploration SpAce Robot (CAESAR) is a light-weight, dexterous robot with seven degrees of freedom designed for on-orbit servicing
