Tag: dynamics
-
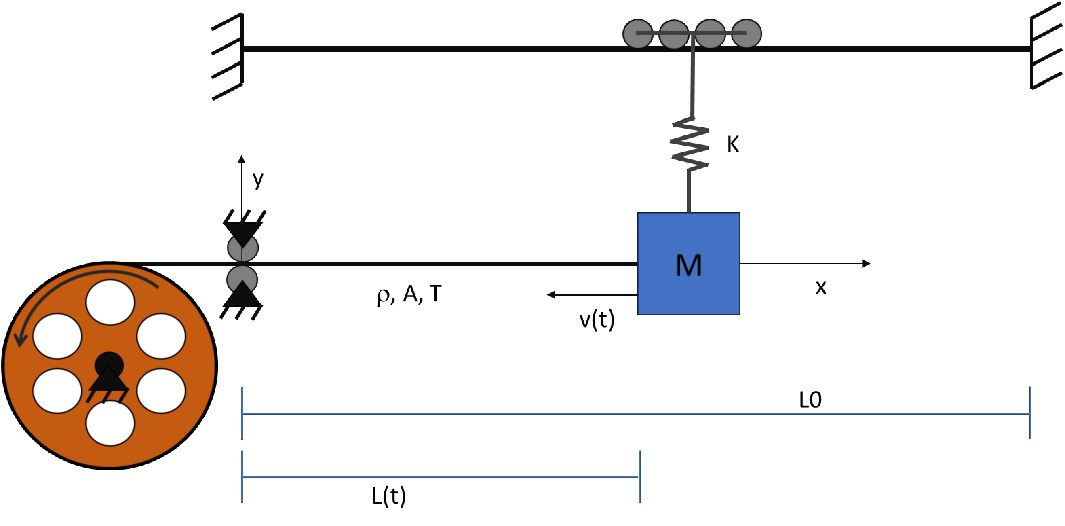
Dynamics of an aerial cableway through a time-varying meshing finite element approach
Ropeways have been used intensively for transportation of goods and people since the early nineteenth century. To study the nonlinear effects of the forces acting on the carrying cable, and how they affect the static and dynamic behaviour of the plant, a finite element model with a time-varying mesh has been developed. The system modelling
-
Study and Optimization of Automotive Suspension Systems Considering Nonlinear Dynamics
Automotive suspension systems play a fundamental role in determining vehicle ride comfort, road holding, and overall handling performance. Modern vehicles operate over a wide range of driving conditions in which suspension components exhibit significant nonlinear behavior due to geometric effects, nonlinear stiffness characteristics, damping properties, and the interaction with road irregularities. The aim of this
-

Actuator Modeling
Introduction Recent advances in GPU-based physics simulation and deep Reinforcement Learning (RL) have enabled the rapid training of control policies for complex, highly articulated robots such as quadrupeds and humanoids. Parallelized simulators now make it possible to obtain policies that transfer to hardware in a matter of minutes of simulated experience [1]. Despite this progress,
-

Macro-mechanical sectional modelling of ballast settlement phenomenon
Optimized management of railway networks, facing growing travelling loads and ageing of track components, requires a thorough understanding of degradation processes. Given ballast complex behaviour, its degradation is particularly critical in track maintenance management. The thesis focuses on the development and refinement of a macro-mechanical cross-sectional model that can reproduce ballast settlement under long-term cyclic
-
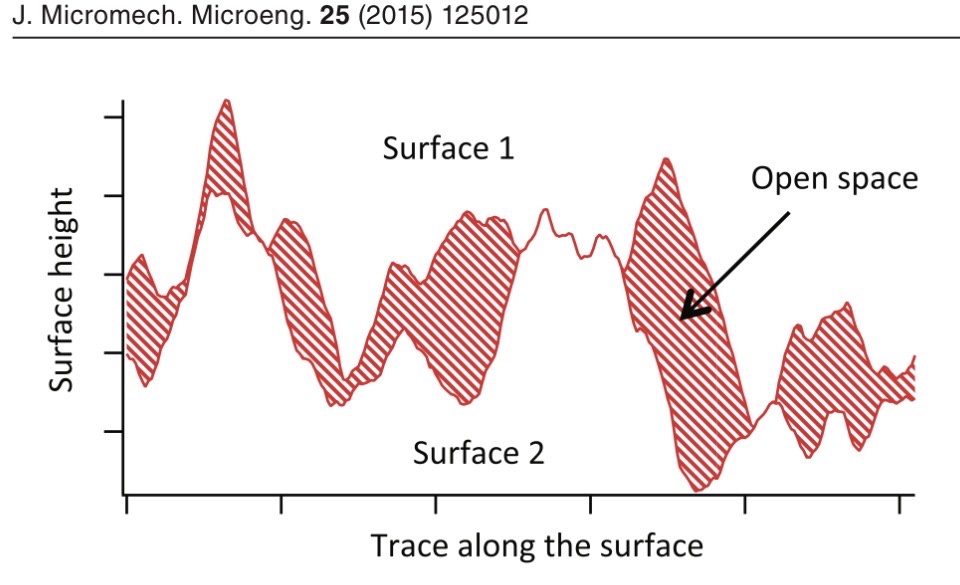
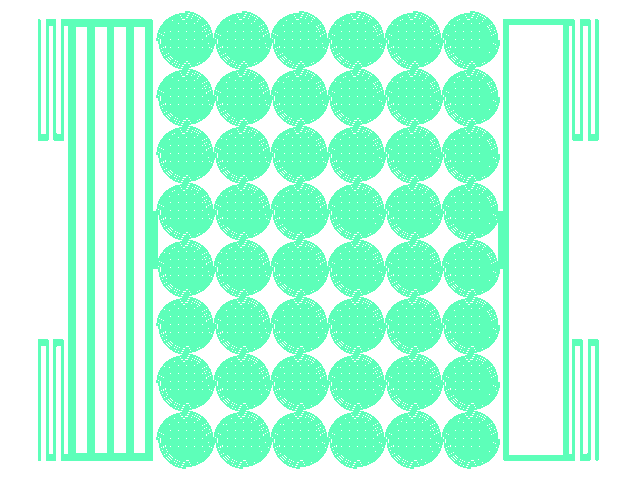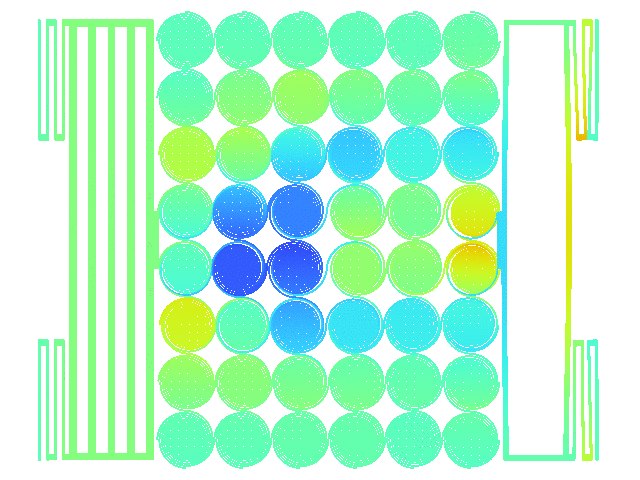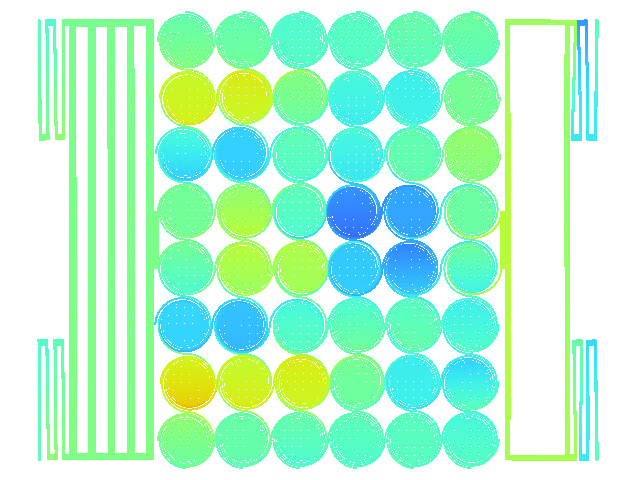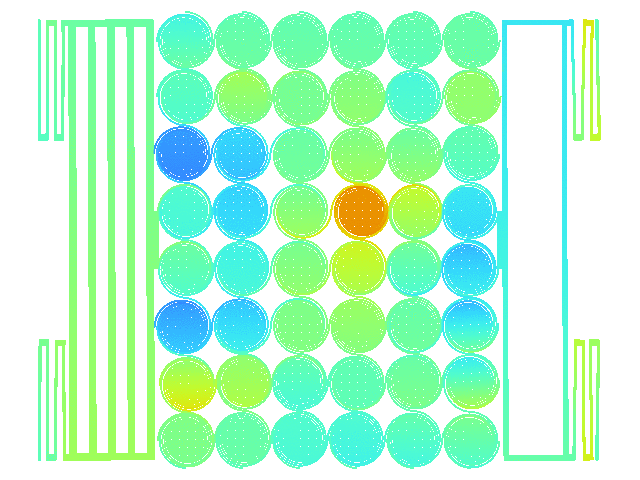
Design of MEMS structure for adhesion characterization
Stiction is a critical phenomenon in MEMS structure which consists in the movable MEMS structure being unable to release from fixed structure when engaged. Stiction depends on many physical mechanisms but can be simplified to a negative balance between restoring forces which try to unstuck the movable mass and the adhesion forces which keep the
-
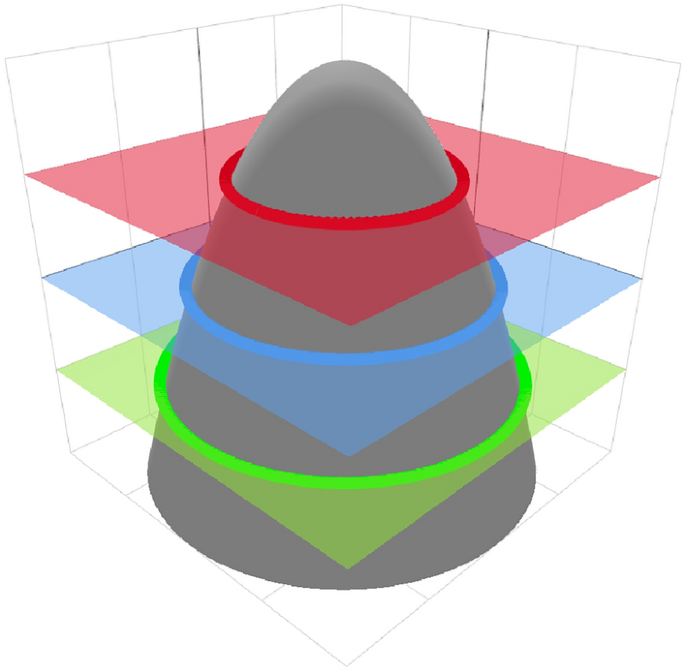
Level-set robust topological optimization applied to MEMS accelerometers
MEMS technology is becoming increasingly important for several inertial applications (e.g., gyroscopes and accelerometers devices). The objective of this thesis is to improve the layout of an existing MEMS accelerometer by implementing level-set topology optimization algorithms in existing software written in C++. Robust techniques will be implemented as well in order to minimize the influence
-
feMEMS: parametric optimization using semi-lumped parameter models
The design of MEMS devices usually involves several Finite Element (FE) analyses, each with different parameters (e.g. beam thicknesses) to tune the characteristics of the sensor. This trial-and-error procedure is tedious and time-consuming, even more so considering that typical FE models may count 100k-1M degrees of freedom. For this reason, our group developed a Matlab