-
The influence of resilient wheels on railway noise and vibration induced by urban rolling stocks
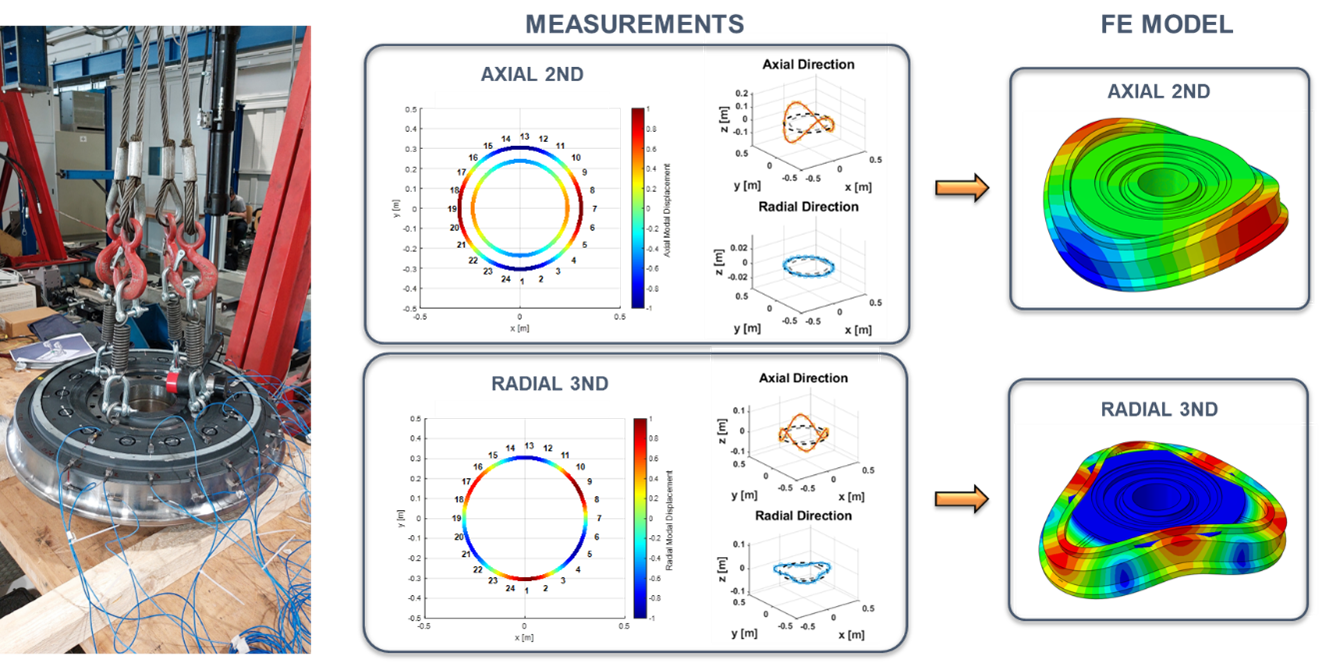
Noise and vibration generated by rail vehicles has become an issue of increasing concern, particularly in urban and interurban contexts where the demand for sustainable and efficient mobility has driven the expansion of rail networks. Nowadays, it is very common to mount resilient wheels on light rail systems or tramcars, with the aim of reducing Read more
-
Mitigation of railway noise using wheel/rail dampers
curve squeal, dampers, FE model, Railway noise, vehicle dynamics, Vibrations, Wheel-Rail interactionNoise and vibration generated by rail vehicles has become an issue of increasing concern, particularly in urban and interurban contexts where the demand for sustainable and efficient mobility has driven the expansion of rail networks. Several mitigation solutions have been developed in the recent years, involving noise barriers, sound absorbing materials, advanced track components, resilient Read more
-
Railway noise: auralization of the sound radiated from wheel and rail
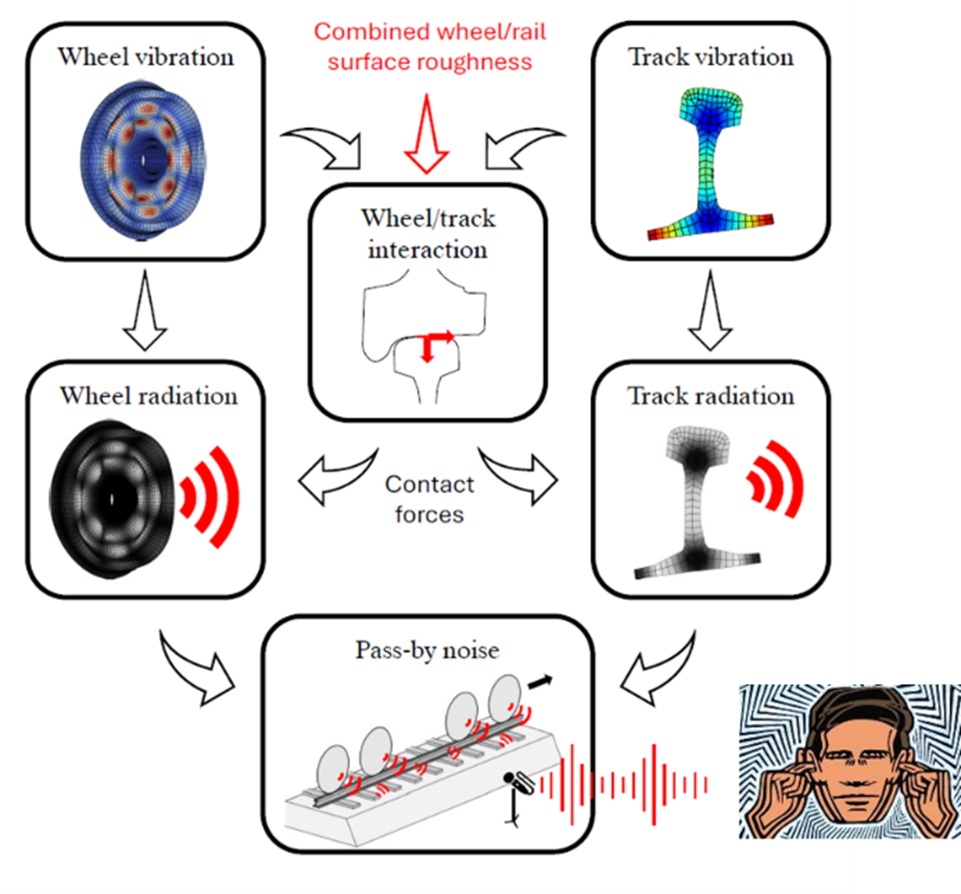
acoustics, auralization, curve squeal, noise synthesis, Railway noise, vehicle dynamics, Wheel-Rail interactionNoise generated by rail vehicles has become an issue of increasing concern, particularly in urban and interurban contexts where the demand for sustainable and efficient mobility has driven the expansion of rail networks. This has led, in recent years, to the development of several methodologies aimed at predicting the noise generated by wheel–rail interaction. However, Read more
-
Railway noise: modelling sound radiation from wheel and rail
Noise generated by rail vehicles has become an issue of increasing concern, particularly in urban and interurban contexts where the demand for sustainable and efficient mobility has driven the expansion of rail networks. Consequently, there is a growing need to optimise vehicle design and component performance to comply with stringent regulatory requirements and to enhance Read more
-
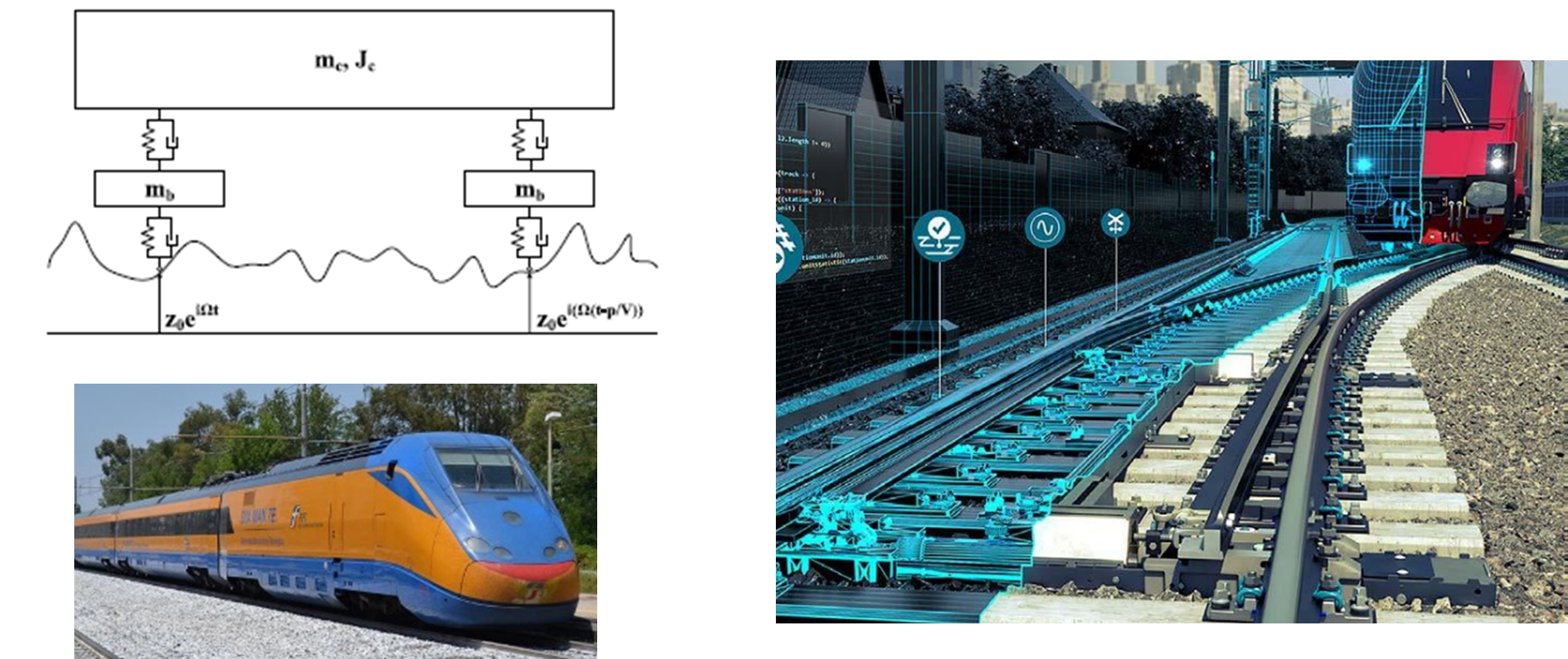
Integration of Physics-Informed and Data-Driven approaches to monitor the railway infrastructure
The rapid development of Artificial Intelligence (AI) has enabled powerful tools for processing large-scale data and extracting meaningful insights across multiple engineering fields. In railway engineering, AI techniques are increasingly being applied to infrastructure monitoring, with the goal of improving safety, reliability, and cost efficiency by detecting defects and predicting maintenance needs more effectively than Read more
-
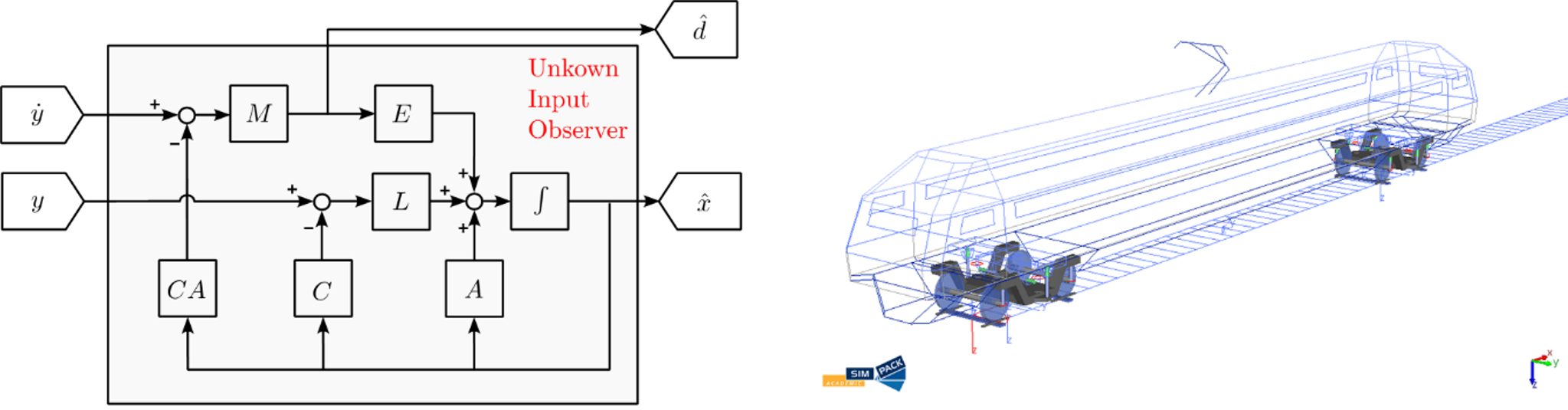
Extension of the Unknown Input Observer algorithm for the identification of lateral railway trackirregularity
To ensure the safety of the railway network, track geometry is periodically inspected by Track Recording Vehicles (TRVs), which are special purpose vehicles typically equipped with inertial and optical sensors. Given their high operating costs, new strategies have been proposed in the latest years to support the condition monitoring of railway infrastructure, relying on instrumented Read more
-
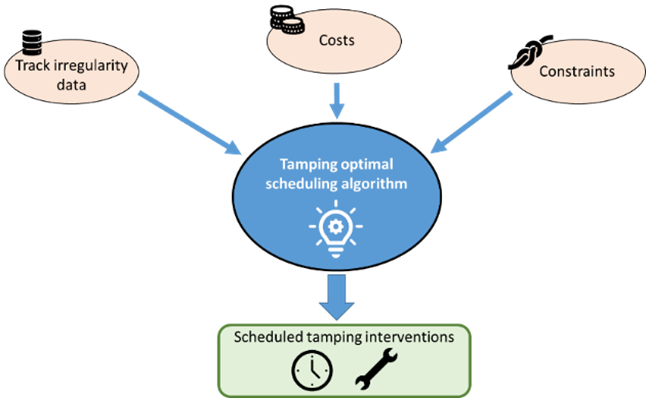
Ballast degradation analysis for optimal tamping scheduling and management
Optimised management of railway networks, subjected to increasing travelling loads and degradation of track components, requires deep understanding and analysis of degradation phenomena. Ballast differential settlement causes an increase in track geometrical irregularity, decreasing passenger’s comfort, and can cause local failure of the railway line. The focus of this thesis work is the analysis of Read more
-
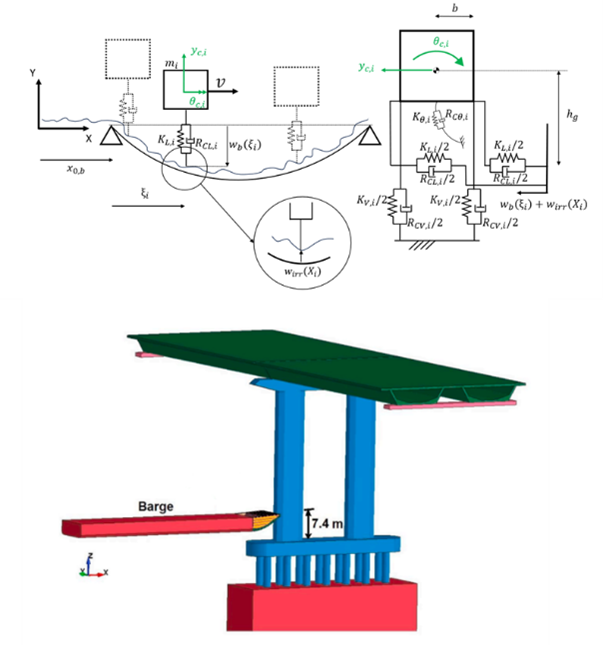
Simplified 2D VBI model to study train safety during ship-bridge impact events
Over the past two decades, the growth of maritime traffic and the increasing number of sea-crossing bridges have emphasized the importance of accounting for ship-impact during bridge design. In runability analyses for train running safety evaluation, vessel-bridge collisions must be incorporated. To manage the large number of simulation required, simplified models of vehicle-bridge-interaction (VBI) can Read more
-
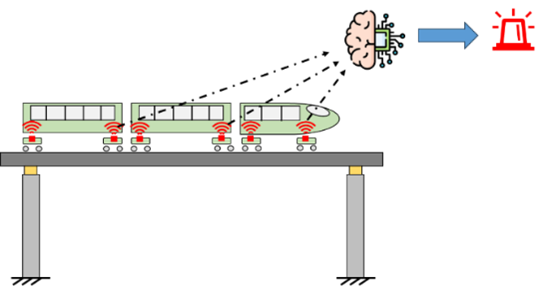
Drive-by techniques for railway bridge structural health monitoring
Drive-by approaches aim to assess bridge structural health status exploiting on-board train measurements. Precisely, damage occurrence on the bridge can be reflected in the dynamic interaction between the train and the bridge itself, and thus in the train response. The focus of this thesis is to improve previously developed signal processing procedures to develop and Read more
-
Macro-mechanical sectional modelling of ballast settlement phenomenon
Optimized management of railway networks, facing growing travelling loads and ageing of track components, requires a thorough understanding of degradation processes. Given ballast complex behaviour, its degradation is particularly critical in track maintenance management. The thesis focuses on the development and refinement of a macro-mechanical cross-sectional model that can reproduce ballast settlement under long-term cyclic Read more