Tag: Machine Learning
-
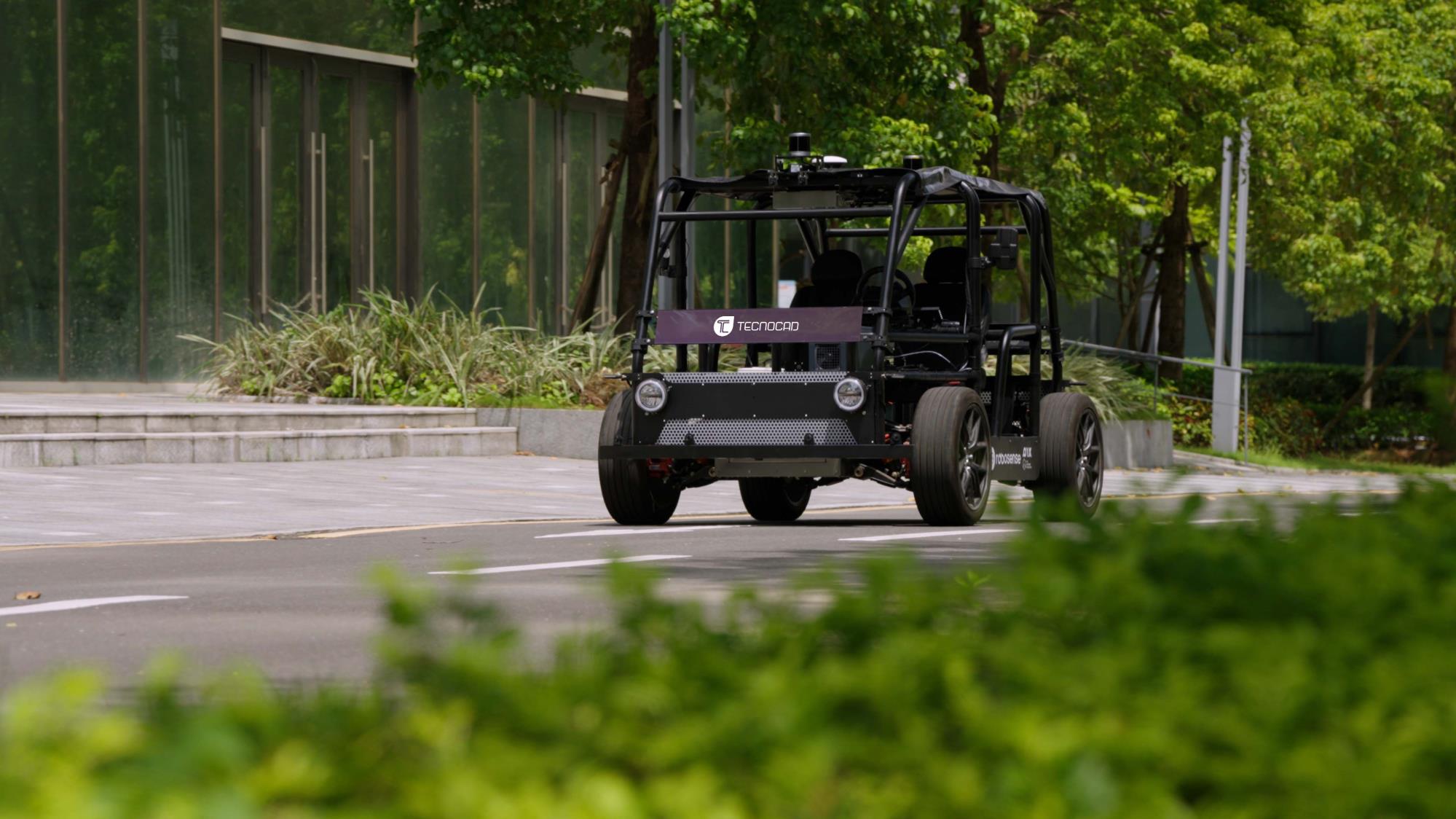

Industry-Driven Topics in AV Software, Teleoperation and Fleet Management with Tecnocad Group
Introduction This thesis “umbrella” is developed in interaction with Tecnocad Group, an Italian engineering company operating across mobility sectors and providing end-to-end engineering development from concept to production.Tecnocad Group delivered a guest presentation within the course, outlining several industry-relevant directions that can be shaped into a thesis topic depending on the interests and technical profile
-
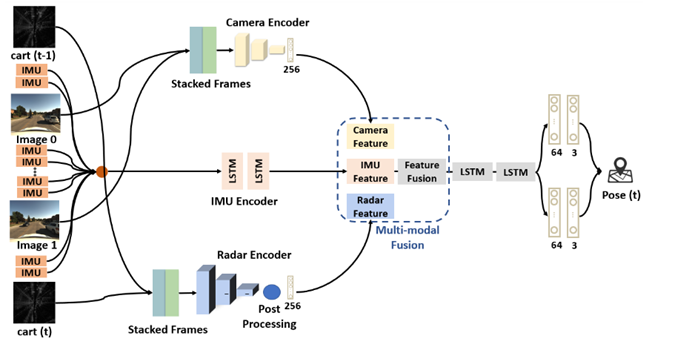
Dataset-Driven Robust Ego Localization for Autonomous Vehicles in Challenging Sensing Conditions
Introduction Robust ego-vehicle localization is a core requirement for autonomous driving. In real-world operation, performance can degrade due to adverse weather and non-ideal sensor behavior, such as dropouts, partial failures, miscalibration, or temporal misalignment. This thesis topic focuses on dataset-driven, learning-based approaches to improve localization robustness in multi-sensor settings, with systematic experimental evaluation. Goals This
-

Adaptive Collision Avoidance in Mixed-Traffic Autonomous Driving via Hamilton-Jacobi Reachability and Learning-Based Techniques
Introduction When it comes to the safety of autonomous vehicles (AV), developing algorithms that balance conservatism and performance is the key to achieve methods that allow Avs to be integrated with human driven ones.One of the most promising techniques is the Hamilton-Jacobi (HJ) backward reachability analysis (based on dynamic programming and differential games), which allows
-

Comparing Modern AI-Powered 3D Reconstruction Pipelines with Traditional Human Motion Capture Systems
Contacts: Marta Gandolla, Andrea Dal Prete Location: Politecnico di Milano (Bovisa Campus) Motivation of the study: Accurate human kinematics measurement is fundamental in biomechanics, ergonomics, and human–robot interaction, yet traditional approaches remain limited. Optical motion capture systems deliver high accuracy but require expensive equipment and controlled laboratory conditions, while IMU-based methods offer portability at the cost of
-
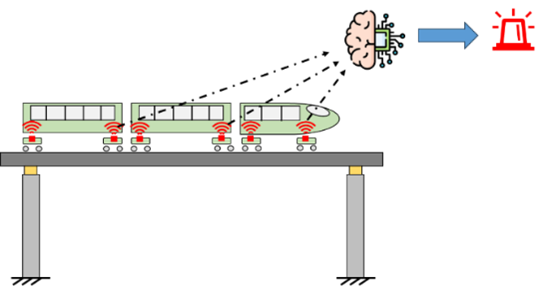
Drive-by techniques for railway bridge structural health monitoring
Drive-by approaches aim to assess bridge structural health status exploiting on-board train measurements. Precisely, damage occurrence on the bridge can be reflected in the dynamic interaction between the train and the bridge itself, and thus in the train response. The focus of this thesis is to improve previously developed signal processing procedures to develop and
-

Data-Driven Structural Health Monitoring of Railway Bridges through Signal Decomposition Methods
Anomaly detection, Machine Learning, Railway bridges, Signal processing, structural health monitoringContacts: Viviana Giorgi, Gabriele Cazzulani, Claudio Somaschini Structural health monitoring of bridges and viaducts is crucial to ensure safety and operational reliability. A promising approach relies on the analysis of acceleration signals recorded during train passages, which contain valuable information about the structural dynamic state. However, extracting robust diagnostic indicators from such high-frequency signals is challenging due to
