-
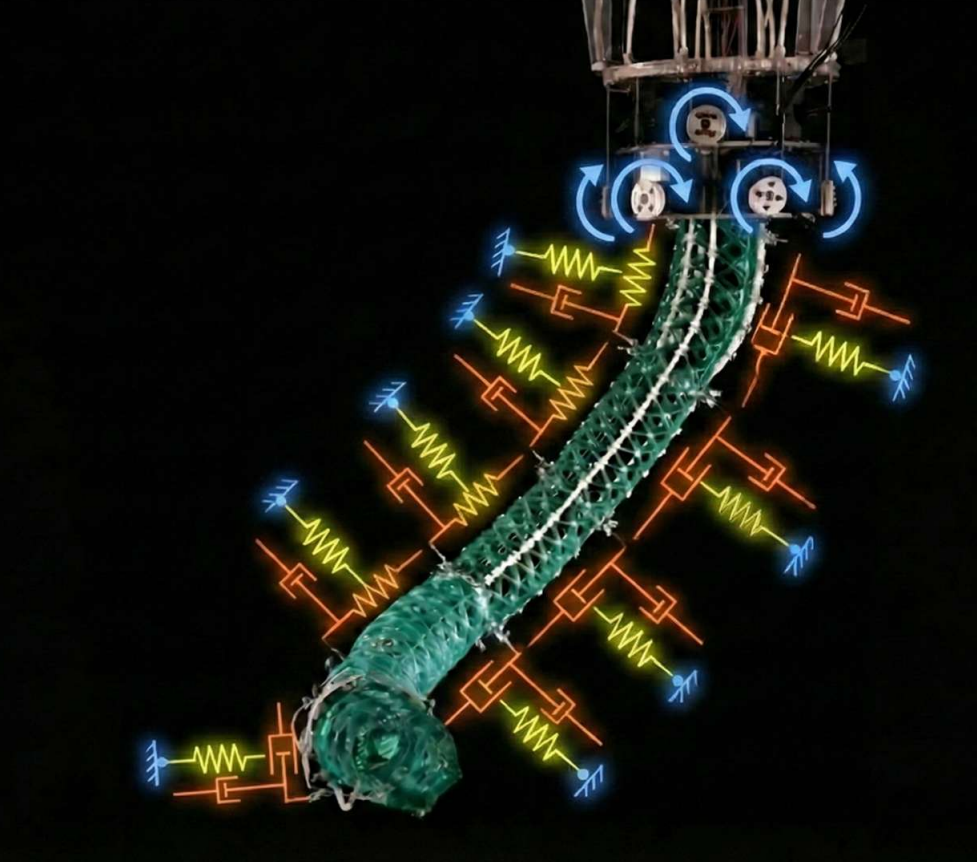
Virtual Model Control of a Soft Compliant Manipulator
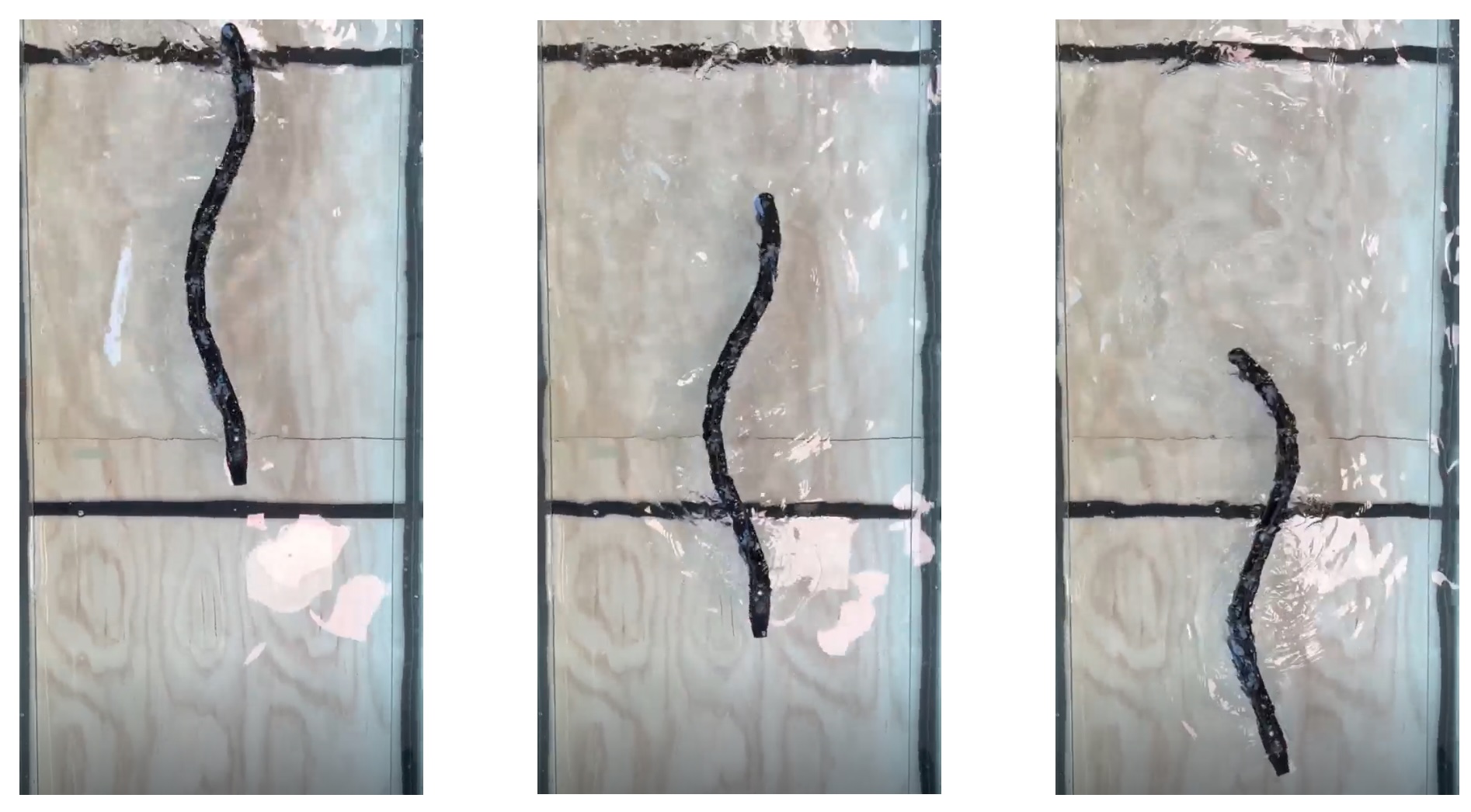
Soft continuum robotic arms offer unparalleled dexterity and compliance over rigid bodies, thus facilitating safe and robust interactions with environments. These characteristics make them ideal for diverse applications, such as collaborative robotics or medical contexts. However, due to their virtually infinite degrees of freedom, control of these systems has always been a challenge. Various control Read more
-
Control of an aquatic snake robot inspired by lampreys’ Central Pattern Generator
Aquatic robots inspired by snakes or eels can move with extreme agility and maneuverability, and are able to swim through narrow spaces and confined environments, opening the possibility to use these robots for environmental monitoring, search and rescue or infrastructure inspection. This robot is composed of nine modules that move generating a wave traveling from Read more
-
Real-time optimal transport of robotic swarms in fluids in 3D domains
Optimally guiding large-scale swarms of drones, underwater vehicles or nanoparticles moving in a fluid is a crucial task in several fields, ranging from medicine to smart delivery. To steer the swarm dynamics avoiding obstacles, controllers must be able to rapidly adapt the optimal action to changes in the external environment, as often happen in applications. Read more
-
Design and testing of an SMA-actuated fin for bioinspired soft robots
The thesis consists of designing a fin inspired by the cownose ray, entirely made of silicone rubber, without any rigid mechanism inside, and actuated by SMA (Shape Memory Alloy) coils. The lack of rigid elements inside the fin helps reproduce better the natural movement of these fishes, and arranging the coils in pairs, they work Read more
-
Study of the propulsive performance of fins
The most common propulsive strategy of fishes and cetaceans is the Body-Caudal fin movement in which the animal undulates or oscillates its body, pushing backward the surrounding water. Most of the thrust is generated by the movement of the caudal fin, and every fish has a peculiar fin shape with a particular motion law, which Read more