Author: Michele Vignati
-
Experimental Study and Validation of Strain-Gauge-Based Smart Tires for Contact Force Estimation
The work is carried out in cooperation with an industrial partner. This thesis activity is aimed at the study and experimental validation of smart tires based on strain-gauge technology for the direct measurement of structural deformations, as an alternative or complement to other technologies like accelerometers. The work includes the integration of large-deformation strain gauges
-
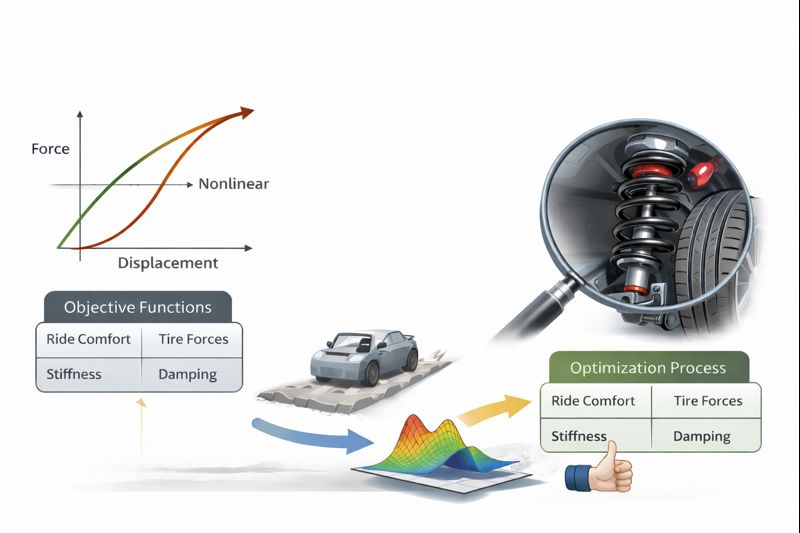
Study and Optimization of Automotive Suspension Systems Considering Nonlinear Dynamics
Automotive suspension systems play a fundamental role in determining vehicle ride comfort, road holding, and overall handling performance. Modern vehicles operate over a wide range of driving conditions in which suspension components exhibit significant nonlinear behavior due to geometric effects, nonlinear stiffness characteristics, damping properties, and the interaction with road irregularities. The aim of this
-
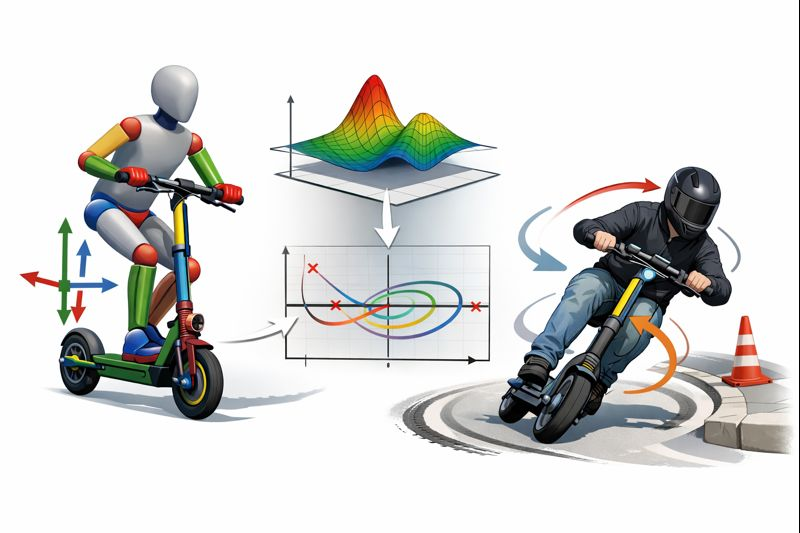
Lateral Dynamics and Stability Analysis of Electric Scooters
The rapid diffusion of electric scooters as a means of urban transportation has raised significant concerns regarding their dynamic stability and rider safety, particularly in lateral maneuvers such as cornering, obstacle avoidance, and low-speed balancing. Despite their widespread use, the lateral dynamics of electric scooters remain less investigated than those of motorcycles or bicycles, especially
-
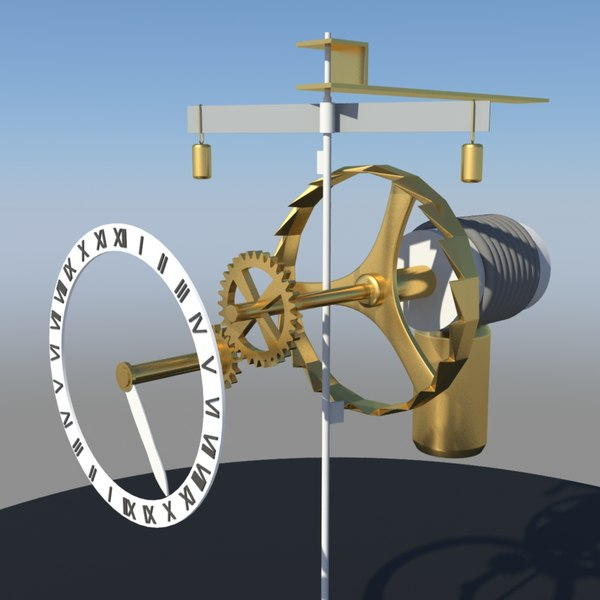
Multibody simulation of medieval mechanical clock
Background and MotivationThe verge-and-foliot escapement is among the earliest mechanical regulation mechanisms, yet its motion and timekeeping performance remain challenging to predict quantitatively because the device operates through intermittent contact between the crown wheel teeth and the pallets mounted on the verge. From an engineering standpoint, this makes the system highly sensitive to geometry, inertia
-
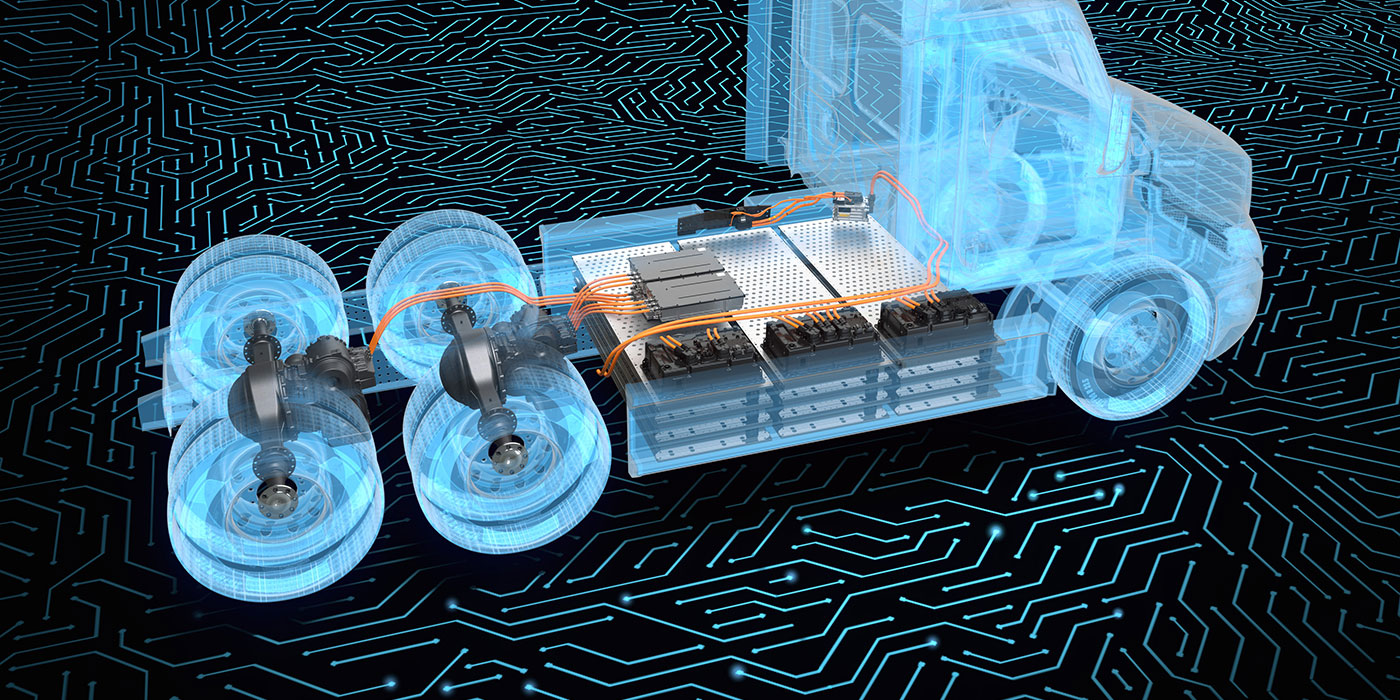
Modeling and control of hybrid powertrain for heavy duty vehicles
This thesis focuses on the modeling and control of hybrid powertrains for heavy-duty vehicles. A comprehensive dynamic model of the powertrain is developed, accounting for the interaction between the internal combustion engine, electric machines, energy storage system, and transmission. Control strategies for power split, energy management, and drivability optimization are investigated under representative operating conditions.
-
Non-linear analysis of powertrain torsional vibration accounting for backlash
This thesis investigates the non-linear torsional vibration behavior of automotive powertrains, explicitly accounting for backlash effects in transmission components. A lumped-parameter dynamic model is developed to represent dead-zone non-linearities, intermittent contact, and impact phenomena. Time- and frequency-domain analyses are performed to study the influence of operating conditions, torque excitation, and system parameters on the dynamic
